博文
ABBS: One-step high-efficiency CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome
||
One-step high-efficiency CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing in Streptomyces
He Huang, Guosong Zheng, Weihong Jiang, Haifeng Hu and Yinhua Lu
Key Lab of Synthetic Biology, Institute of Plant Physiology and Ecology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200032, China
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 2015, 47: 231–243; doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmv007
The RNA-guided DNA editing technology CRISPRs (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)/Cas9 had been used to introduce double-stranded breaks into genomes and to direct subsequent site-specific insertions/deletions or the replacement of genetic material in bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, Streptococcus pneumonia, and Lactobacillus reuteri. In this study, we established a high-efficiency CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing plasmid pKCcas9dO for use in Streptomyces genetic manipulation, which comprises a target-specific guide RNA, a codon-optimized cas9, and two homology-directed repair templates. By delivering pKCcas9dO series editing plasmids into the model strain Streptomyces coelicolor M145, through one-step intergeneric transfer, we achieved the genome editing at different levels with high efficiencies of 60%–100%, including single gene deletion, such as actII-orf4, redD, and glnR, and single large-size gene cluster deletion, such as the antibiotic biosynthetic clusters of actinorhodin (ACT) (21.3 kb), undecylprodigiosin (RED) (31.6 kb), and Ca2+-dependent antibiotic (82.8 kb). Furthermore, we also realized simultaneous deletions of actII-orf4 and redD, and of the ACT and RED biosynthetic gene clusters with high efficiencies of 54% and 45%, respectively. Finally, we applied this system to introduce nucleotide point mutations into the rpsL gene, which conferred the mutants with resistance to streptomycin. Notably, using this system, the time required for one round of genome modification is reduced by one-third or one-half of those for conventional methods. These results clearly indicate that the established CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing system substantially improves the genome editing efficiency compared with the currently existing methods in Streptomyces, and it has promise for application to genome modification in other Actinomyces species.
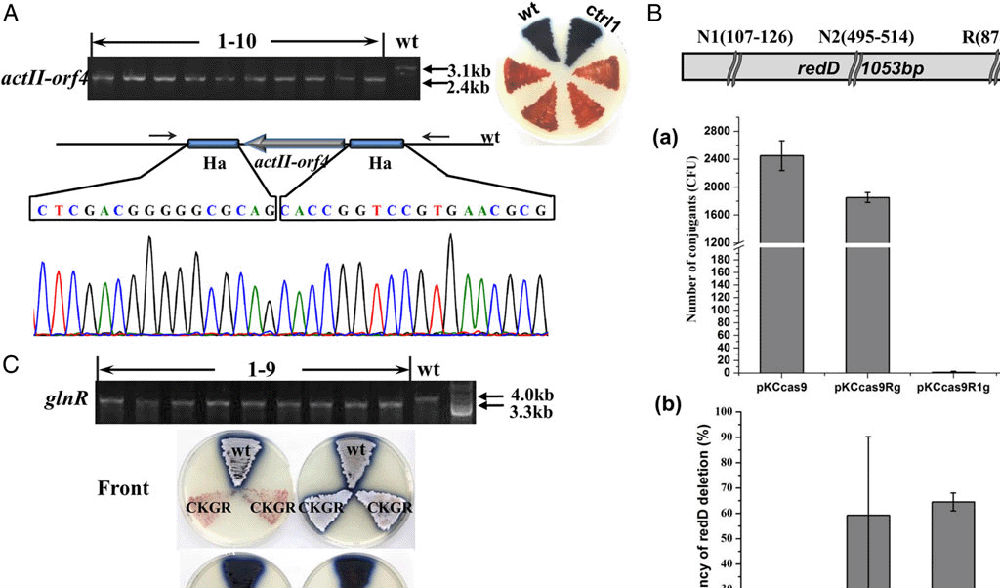
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated single gene deletions
全文: http://www.abbs.org.cn/arts.asp?id=3845
相关论文:
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-592748-965713.html
上一篇:ABBS: Hypoxia promotes bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
下一篇:ABBS: Pannexin-1 channels and their emerging functions in ca