博文
大连化物所刘中民院士为FCSE组织专题:催化科学与技术前沿
|
近年来,随着能源和环境领域的快速发展与进步,催化科学与技术得到了极大的发展。能源是国际与国内社会经济发展共同关注的世界性重要问题之一。很多情况下,能源或含有能源的材料需要被转化为更有价值的形式或状态。催化在几乎所有转化过程中都起着核心的作用,比如:炼油、煤炭加工利用、燃料电池、储能、氢的制备与存储、太阳能利用以及生物质转化等。此外,催化在环境保护中也起着十分重要的作用,比如:温室气体排放、水净化、二氧化碳捕集和转化等。因此,Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering (FCSE)邀请到中科院大连化学物理研究所所长刘中民院士为我们组织了“催化科学与技术前沿”专题,旨在报道相关领域激动人心的研究进展与成果。
在本期专题里,我们刊发了来自国内外研究小组的4篇综述和11篇研究论文。这些文章覆盖面广,主要集中在新工艺的开发、新催化剂的发现、制备催化剂的新方法,以及催化剂在石油炼制、加氢精制、烯烃和PX生产,生物质转化,H2O2制备、NO还原和CO2分离/捕集中的应用。这反映了催化科学与技术的多学科特征。具体文章如下:
| EDITORIAL |
Frontiers of Catalysis Chemistry and TechnologyDOI: 10.1007/s11705-018-1704-0 Cite this article: . Frontiers of Catalysis Chemistry and Technology[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 1 -2 |
| COMMUNICATION |
Mild and highly regioselective synthesis of biaryl acids via Rh(I)-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenative coupling of benzoic acids using sodium chlorite as oxidantDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1693-4 Yun Liu, Youquan Zhu, Chaojun Li Abstract: A mild and efficient synthesis for the biaryl acids via rhodium-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenative coupling reaction has been developed. This novel protocol with sodium chlorite as an oxidant featured many advantages such as mild reaction conditions, high regioselectivity, tolerance of various functional groups, and good to excellent yields. Cite this article: Yun Liu, Youquan Zhu, Chaojun Li. Mild and highly regioselective synthesis of biaryl acids via Rh(I)-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenative coupling of benzoic acids using sodium chlorite as oxidant[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 3 -8 |
| VIEWS & COMMENTS |
A novel fluid catalytic cracking process for maximizing iso-paraffins: From fundamentals to commercializationDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1696-1 Youhao Xu, Shouye Cui Abstract: The maximizing iso-paraffins (MIP) developed by RIPP has improved gasoline quality to meet the demand of motor gasoline specification. A concept that two different reaction zones include cracking zone and conversion zone is proposed as the fundamental of MIP by research on fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) reaction chemistry. Based on the concept, the MIP process is featured by applying a novel sequential two-zone riser in conjunction with proprietary catalyst and engineering technique. The developed MIP process can not only improve gasoline yield or gasoline plus propylene yields but also produce gasoline with a higher content of iso-paraffins and a lower content of sulfur. A minimum octane number loss is achieved when MIP gasoline is treated by downstream desulfurization technology (RSDS/S Zorb). The combination of MIP and RSDS/S Zorb processes creates a very competitive route, which is different from the technical route used by other developed countries, to upgrade the quality of motor gasoline with the lowest economic costs in China. In just one decade, the processing capacity of MIP units has accounted for about 60% of the domestic total processing capacity of FCC units. The MIP process is gradually becoming a new generation of FCC technology. Cite this article: Youhao Xu, Shouye Cui. A novel fluid catalytic cracking process for maximizing iso-paraffins: From fundamentals to commercialization[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 9 -23 |
| RESEARCH ARTICLE |
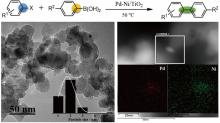
Pd-Ni nanoparticles supported on titanium oxide as effective catalysts for Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactionsDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1669-4 Dongxu Han, Zhiguo Zhang, Zongbi Bao, Huabin Xing, Qilong Ren Abstract: We have successfully prepared a series of Pd-Ni/TiO2 catalysts by a one-step impregnation-reduction method. Among these catalysts with different compositions of Ni and Pd, the one with the Ni:Pd ratio of 2.95 showed the best activity. Small monodispersed Pd-Ni bimetallic nanoparticles were loaded on the surface of titanium oxide nanopowder as confirmed with TEM and EDS mapping. The XPS analysis demonstrated that Pd exists as 31% Pd(II) species and 69% Pd(0) species and all nickel is Ni(II). The prepared Pd-Ni/TiO2 exhibited enhanced catalytic activity compared to an equal amount of Pd/TiO2 for Suzuki-Miyaura reactions together with excellent applicability and reusability. Cite this article: Dongxu Han, Zhiguo Zhang, Zongbi Bao, Huabin Xing, Qilong Ren. Pd-Ni nanoparticles supported on titanium oxide as effective catalysts for Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 24 -31 |
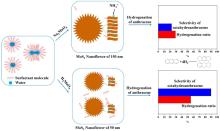
Microemulsion-mediated hydrothermal synthesis of flower-like MoS2 nanomaterials with enhanced catalytic activities for anthracene hydrogenationDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1677-4 Yuxia Jiang, Donge Wang, Zhendong Pan, Huaijun Ma, Min Li, Jiahe Li, Anda Zheng, Guang Lv, Zhijian Tian Abstract: Flower-like intercalated MoS2 nanomaterials have been successfully synthesized via a microemulsion-mediated hydrothermal (MMH) method, and characterized by X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, element analysis, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy in detail. Their catalytic performance for anthracene hydrogenation was evaluated using a slurry-bed batch reactor with an initial hydrogen pressure of 80 bar at 350 °C for 4 h. The intercalated MoS2nanoflowers synthesized from Na2MoO4 (MoS2-S) and H2MoO4 (MoS2-A) as molybdenum precursors have diameters of about 150 and 50 nm, respectively. MoS2 nanosheets on MoS2-S and MoS2-A possess stacking layer numbers of 5–10 and 2–5, and slab lengths of about 15 and 10 nm, respectively. The interlayer distances of MoS2-S and MoS2-A are both enlarged from 0.62 nm to about 0.95 nm due to the intercalation of NH4+ and surfactant molecules. The MoS2 nanoflowers have high catalytic activities for anthracene hydrogenation. The selectivity for octahydroanthracene, a deeply hydrogenated product, over MoS2-A is 89.8%, which is 31.0 times higher than that over commercial bulk MoS2. Fully hydrogenated product (perhydroanthracene) was also detected over MoS2 nanoflowers with a selectivity of 3.7%. The enhanced hydrogenation activities of MoS2 nanoflowers can be ascribed to the high exposure of catalytic active sites, resulting from the smaller particle size, fewer stacking layer, shorter slab length and enlarged interlayer distance of MoS2 nanoflowers compared with commercial bulk MoS2. In addition, a possible growth mechanism of MoS2 nanoflowers synthesized via the MMH method was proposed. Cite this article: Yuxia Jiang, Donge Wang, Zhendong Pan, Huaijun Ma, Min Li, Jiahe Li, Anda Zheng, Guang Lv, Zhijian Tian. Microemulsion-mediated hydrothermal synthesis of flower-like MoS2 nanomaterials with enhanced catalytic activities for anthracene hydrogenation[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 32 -42 |
Template-free synthesis of hierarchically macro-mesoporous Mn-TiO2 catalysts for selective reduction of NO with NH3DOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1679-2 Zhao Peng, Li-Hua Chen, Ming-Hui Sun, Pan Wu, Chang Cai, Zhao Deng, Yu Li, Wei-Hong Zheng, Bao-Lian Su Abstract: This study described a template-free method for the synthesis of hierarchically macro-mesoporous Mn-TiO2 catalysts. The promoting effect of Mn doping and the hierarchically macro-mesoporous architecture on TiO2 based catalysts was also investigated for the selective reduction of NO with NH3. The results show that the catalytic performance of TiO2 based catalysts was improved greatly after Mn doping. Meanwhile, the Mn-TiO2 catalyst with the hierarchically macro-mesoporous architecture has a better catalytic activity than that without such an architecture. Cite this article: Zhao Peng, Li-Hua Chen, Ming-Hui Sun, Pan Wu, Chang Cai, Zhao Deng, Yu Li, Wei-Hong Zheng, Bao-Lian Su. Template-free synthesis of hierarchically macro-mesoporous Mn-TiO2catalysts for selective reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 43 -49 |
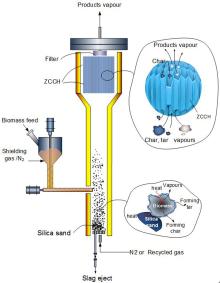
Upgrading of derived pyrolysis vapors for the production of biofuels from corncobsDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1685-4 Liaoyuan Mao, Yanxin Li, Z. Conrad Zhang Abstract: A bubbling fluidized bed pyrolyzer was integrated with an in-situ honeycomb as a catalytic upgrading zone for the conversion of biomass to liquid fuels. In the upgrading zone, zeolite coated ceramic honeycomb (ZCCH) catalysts consisting of ZSM-5 (Si/Al=25) were stacked and N2 or recycled non-condensable gas was used as a carrier gas. Ground corncob particles were fast pyrolyzed in the bubbling bed using fine sand particles as a heat carrier and the resulting pyrolysis vapors were passed on-line over the catalytic upgrading zone. The influence of carrier gas, temperature, and weight hourly space velocity (WHSV) of catalyst on the oil product properties, distribution and mass balance were studied. Using ZCCH effectively increased the hydrocarbon yield and the heating value of the dry oil, especially in the presence of the recycled noncondensable gas. Even a low usage of zeolite catalyst at WSHV of 180 h−1 was effective in upgrading the pyrolysis oil and other light olefins. The highest hydrocarbon (≥C2) and liquid aromatics yields reached to 14.23 and 4.17 wt-%, respectively. The undesirable products including light oxygenates, furans dramatically decreased in the presence of the ZCCH catalyst. Cite this article: Liaoyuan Mao, Yanxin Li, Z. Conrad Zhang. Upgrading of derived pyrolysis vapors for the production of biofuels from corncobs[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 50 -58 |
Tuning of the active phase structure and hydrofining performance of alumina-supported tri-metallic WMoNi catalysts via phosphorus incorporationDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1686-3 Shufeng Shan, Haiyan Liu, Gang Shi, Xiaojun Bao Abstract: The effects of phosphorus on the structure and hydrofining performance of tri-metallic WMoNi/Al2O3 catalysts prepared with W/Mo-based hybrid precursor nanocrystals were investigated. The incorporation of phosphorus weakened the metal-support interactions (MSIs) and facilitated the formation of more synergetic NiWMoS phases with higher stacks. Catalytic tests using a fluid catalytic cracking diesel fuel showed that the changes in the MSIs and the morphology of the active phases had a more positive effect on the hydrodenitrogenation activity than on the hydrodesulfurization activity. In contrast, when phosphorus was incorporated into a tri-metallic WMoNiP/Al2O3 catalyst prepared by a conventional incipient impregnation method, the MSIs decreased causing aggregation of the metal species which resulted in poorer hydrofining performance of the catalyst. These results show that incorporating phosphorus into a WMoNi/Al2O3 catalyst can finely tune the structure of the active phase to enhance the hydrogenation and hydrodenitrogenation activity of the resulting tri-metallic catalyst. Cite this article: Shufeng Shan, Haiyan Liu, Gang Shi, Xiaojun Bao. Tuning of the active phase structure and hydrofining performance of alumina-supported tri-metallic WMoNi catalysts via phosphorus incorporation[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 59 -69 |
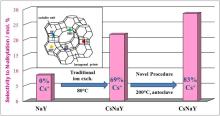
Novel method for the preparation of Cs-containing FAU(Y) catalysts for aniline methylationDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1694-3 Olga A. Ponomareva, Polina A. Shaposhnik, Marina V. Belova, Boris A. Kolozhvari, Irina I. Ivanova Abstract: Cs-containing FAU(Y)-type zeolite catalysts were prepared by conventional and novel ion exchange procedures followed by incipient wetness impregnation with CsOH. The novel ion exchange procedure involved hydrothermal treatment of NaY zeolite in aqueous solution of CsCl at 140–200 °C for 6–24 h. The samples were characterized by low-temperature nitrogen adsorption, X-ray fluorescence analysis, X-ray powder diffraction, scanning electron microscopy,23Na, 27Al and 133Cs magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance, CO2 and NH3-Temperature programmed desorption. The results show that hydrothermal treatment at 200 °C allows to obtain higher degrees of ion-exchange (up to 83%) with respect to conventional method giving maximum 66%–69%. Catalytic properties of Cs-containing FAU(Y) were studied in aniline methylation. The yield of N-methylaniline is shown to correlate with catalyst’s basicity. The best catalyst performance was achieved over the catalyst with the highest ion-exchange degree impregnated with CsOH. The selectivity to N-methylaniline over this catalyst reached 96.4%. Cite this article: Olga A. Ponomareva, Polina A. Shaposhnik, Marina V. Belova, Boris A. Kolozhvari, Irina I. Ivanova. Novel method for the preparation of Cs-containing FAU(Y) catalysts for aniline methylation[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 70 -76 |
High-precision diffusion measurement of ethane and propane over SAPO-34 zeolites for methanol-to-olefin processDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1684-5 Dali Cai, Yu Cui, Zhao Jia, Yao Wang, Fei Wei Abstract: The methanol-to-olefin (MTO) process has attracted much attention and many problems including lifetime and selectivity of light olefins have all been connected to the diffusion problems in zeolite crystals. However, a quantitative study of diffusion problems in SAPO-34 zeolites is lacking. In this paper, we performed a high-precision diffusion measurement of the diffusion behavior of ethane and propane, which represent ethylene and propylene respectively, over SAPO-34. The diffusions of ethane and propane over fresh and coked SAPO-34 zeolites with different crystal sizes were carefully studied. Ethane and propane show different diffusion behavior in SAPO-34. The diffusion of ethane is almost not influenced by the crystal size and coke percentage, whereas that of propane is strongly affected. A slower diffusion velocity was observed in bigger crystals, and the diffusion velocity decline significantly with the coke percentage increasing. The diffusion coefficient was calculated with both the internal and surface diffusion models, and the results show that the surface diffusion plays a key role in the diffusion process of both ethane and propane. We believe that this work would be helpful for understanding the diffusion of different molecules in SAPO-34 zeolites, and may lay the foundation of MTO research. Cite this article: Dali Cai, Yu Cui, Zhao Jia, Yao Wang, Fei Wei. High-precision diffusion measurement of ethane and propane over SAPO-34 zeolites for methanol-to-olefin process[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 77 -82 |
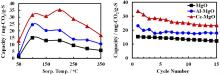
Al2O3 and CeO2-promoted MgO sorbents for CO2 capture at moderate temperaturesDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1691-6 Huimei Yu, Xiaoxing Wang, Zhu Shu, Mamoru Fujii, Chunshan Song Abstract: A series of Al2O3 and CeO2 modified MgO sorbents was prepared and studied for CO2sorption at moderate temperatures. The CO2 sorption capacity of MgO was enhanced with the addition of either Al2O3 or CeO2. Over Al2O3-MgO sorbents, the best capacity of 24.6 mg-CO2/g-sorbent was attained at 100 °C, which was 61% higher than that of MgO (15.3 mg-CO2/g-sorbent). The highest capacity of 35.3 mg-CO2/g-sorbent was obtained over the CeO2-MgO sorbents at the optimal temperature of 200 °C. Combining with the characterization results, we conclude that the promotion effect on CO2 sorption with the addition of Al2O3 and CeO2 can be attributed to the increased surface area with reduced MgO crystallite size. Moreover, the addition of CeO2increased the basicity of MgO phase, resulting in more increase in the CO2 capacity than Al2O3promoter. Both the Al2O3-MgO and CeO2-MgO sorbents exhibited better cyclic stability than MgO over the course of fifteen CO2 sorption-desorption cycles. Compared to Al2O3, CeO2 is more effective for promoting the CO2 capacity of MgO. To enhance the CO2 capacity of MgO sorbent, increasing the basicity is more effective than the increase in the surface area. Cite this article: Huimei Yu, Xiaoxing Wang, Zhu Shu, Mamoru Fujii, Chunshan Song. Al2O3 and CeO2-promoted MgO sorbents for CO2 capture at moderate temperatures[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 83 -93 |
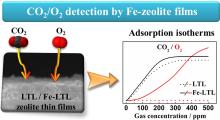
Detection of CO2 and O2 by iron loaded LTL zeolite filmsDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1692-5 Veselina Georgieva, Richard Retoux, Valerie Ruaux, Valentin Valtchev, Svetlana Mintova Abstract: Detection of oxygen and carbon dioxide is important in the field of chemical and biosensors for atmosphere and biosystem monitoring and fermentation processes. The present study reports on the preparation of zeolite films doped with iron nanoparticles for detection of CO2 and O2 in gas phase. Pure nanosized LTL type zeolite with monomodal particle size distribution loaded with iron (Fe-LTL) was prepared under hydrothermal condition from colloidal precursor suspensions. The zeolite was loaded with iron to different levels by ion exchange. The Fe-LTL suspensions were used for preparation of thin films on silicon wafers via spin coating method. The reduction of the iron in the zeolite films was carried out under H2 flow (50% H2 in Ar) at 300 °C. The presence of iron nanoparticles is proved by in situ ultra-violet-visible spectroscopy. The properties of the films including surface roughness, thickness, porosity, and mechanical stability were studied. In addition, the loading and distribution of iron in the zeolite films were investigated. The Fe-LTL zeolite films were used to detect O2 and CO2 in a concentration dependent mode, followed by IR spectroscopy. The changes in the IR bands at 855 and 642 cm−1(Fe–O–H and Fe–O bending vibrations) and at 2363 and 2333 cm−1 (CO2 asymmetric stretching) corresponding to the presence of O2 and CO2, respectively, were evaluated. The response to O2and CO2 was instant, which was attributed to great accessibility of the iron in the nanosized zeolite crystals. The saturation of the Fe-LTL films with CO2 and O2 at each concentration was reached within less than a minute. The Fe-LTL films detected both oxygen and carbon dioxide in contrast, to the pure LTL zeolite film. Cite this article: Veselina Georgieva, Richard Retoux, Valerie Ruaux, Valentin Valtchev, Svetlana Mintova. Detection of CO2 and O2 by iron loaded LTL zeolite films[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 94 -102 |
| REVIEW ARTICLE |
Shape selective catalysis in methylation of toluene: Development, challenges and perspectivesDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1671-x Jian Zhou, Zhicheng Liu, Yangdong Wang, Dejin Kong, Zaiku Xie Abstract: Toluene methylation with methanol offers an alternative method to produce p-xylene by gathering methyl group directly from C1 chemical sources. It supplies a “molecular engineering” process to realize directional conversion of toluene/methanol molecules by selective catalysis in complicated methylation system. In this review, we introduce the synthesis method of p-xylene, the development history of methylation catalysts and reaction mechanism, and the effect of reaction condition in para-selective technical process. If constructing p-xylene as the single target product, the major challenge to develop para-selective toluene methylation is to improve the p-xylene selectivity without, or as little as possible, losing the fraction of methanol for methylation. To reach higher yield of p-xylene and more methanol usage in methylation, zeolite catalyst design should consider improving mass transfer and afterwards covering external acid sites by surface modification to get short “micro-tunnels” with shape selectivity. A solid understanding of mass transfer will benefit realizing the aim of converting more methanol feedstock into para-methyl group. Cite this article: Jian Zhou, Zhicheng Liu, Yangdong Wang, Dejin Kong, Zaiku Xie. Shape selective catalysis in methylation of toluene: Development, challenges and perspectives[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 103 -112 |
A mini review on strategies for heterogenization of rhodium-based hydroformylation catalystsDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1672-9 Cunyao Li, Wenlong Wang, Li Yan, Yunjie Ding Abstract: Hydroformylation has been widely used in industry to manufacture high value-added aldehydes and alcohols, and is considered as the largest homogenously catalyzed process in industry. However, this process often suffers from complicated operation and the difficulty in catalyst recycling. It is highly desirable to develop a heterogeneous catalyst that enables the catalyst recovery without sacrificing the activity and selectivity. There are two strategies to afford such a catalyst for the hydrofromylation: immobilized catalysts on solid support and porous organic ligand (POL)-supported catalysts. In the latter, high concentration of phosphine ligands in the catalyst framework is favorable for the high dispersion of rhodium species and the formation of Rh-P multiple bonds, which endow the catalysts with high activity and stability respectively. Besides, the high linear regioselectivity could be achieved through the copolymerization of vinyl functionalized bidentate ligand (vinyl biphephos) and monodentate ligand (3vPPh3) into the catalyst framework. The newly-emerging POL-supported catalysts have great perspectives in the industrial hydroformylation. Cite this article: Cunyao Li, Wenlong Wang, Li Yan, Yunjie Ding. A mini review on strategies for heterogenization of rhodium-based hydroformylation catalysts[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 113 -123 |
Advances in the slurry reactor technology of the anthraquinone process for H2O2productionDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1676-5 Hongbo Li, Bo Zheng, Zhiyong Pan, Baoning Zong, Minghua Qiao Abstract: This paper overviews the development of the anthraquinone auto-oxidation (AO) process for the production of hydrogen peroxide in China and abroad. The characteristics and differences between the fixed-bed and fluidized-bed reactors for the AO process are presented. The detailed comparison indicates that the production of hydrogen peroxide with the fluidized-bed reactor has many advantages, such as lower operation cost and catalyst consumption, less anthraquinone degradation, higher catalyst utilization efficiency, and higher hydrogenation efficiency. The key characters of the production technology of hydrogen peroxide based on the fluidized-bed reactor developed by the Research Institute of Petroleum Processing, Sinopec are also disclosed. It is apparent that substituting the fluidized-bed reactor for the fixed-bed reactor is a major direction of breakthrough for the production technology of hydrogen peroxide in China. Cite this article: Hongbo Li, Bo Zheng, Zhiyong Pan, Baoning Zong, Minghua Qiao. Advances in the slurry reactor technology of the anthraquinone process for H2O2 production[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 124 -131 |
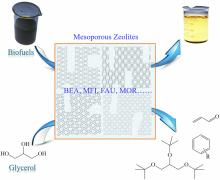
Mesoporous zeolites for biofuel upgrading and glycerol conversionDOI: 10.1007/s11705-017-1681-8 Jian Zhang, Liang Wang, Yanyan Ji, Fang Chen, Feng-Shou Xiao Abstract: With the recent emphasis and development of sustainable chemistry, the conversion of biomass feedstocks into alternative fuels and fine chemicals over various heterogeneous catalysts has received much attention. In particular, owing to their uniform micropores, strong acidity, and stable and rigid frameworks, zeolites as catalysts or co-catalysts have exhibited excellent catalytic performances in many reactions, including hydrodesulfurization, Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, and hydrodeoxygenation. However, the relatively small sizes of the zeolite micropores strongly limit the conversion of bulky biomolecules. To overcome this issue, mesoporous zeolites with pores larger than those of biomolecules have been synthesized. As expected, these mesoporous zeolites have outperformed conventional zeolites with improved activities, better selectivities, and longer catalyst lives for the upgrading of pyrolysis oils, the transformation of lipids into biofuels, and the conversion of glycerol into acrolein and aromatic compounds. This review briefly summarizes recent works on the rational synthesis of mesoporous zeolites and their superior catalytic properties in biomass conversion. Cite this article: Jian Zhang, Liang Wang, Yanyan Ji, Fang Chen, Feng-Shou Xiao. Mesoporous zeolites for biofuel upgrading and glycerol conversion[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018. 12(1): 132 -144 |
https://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-2488407-1103061.html
上一篇:大连理工大学贺高红教授团队介绍膜蒸馏-结晶的研究进展
下一篇:FCSE专题征稿- Fluorescent Probes